Understanding SSL certificates
Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) certificates, commonly known as Transport Layer Security (TLS) certificates, are used to verify the identity of a website and secure data communication between a web server and a browser.
In addition to providing a centralized view of SSL certificates and certificate details, SCM enables appropriately privileged administrators to do the following:
-
Manage certificate lifecycles — Request, renew, replace, and revoke SSL certificates.
-
Manage certificate requests — Approve, decline, and edit SSL certificate requests.
-
Download certificates — Download SSL certificates in various formats.
-
Initiate auto-installation — Initiated configured remote SSL certificate installation.
| For more information on SSL certificates, see What Is an SSL Certificate & How Does It Work. |
SSL certificates can be managed on the page.
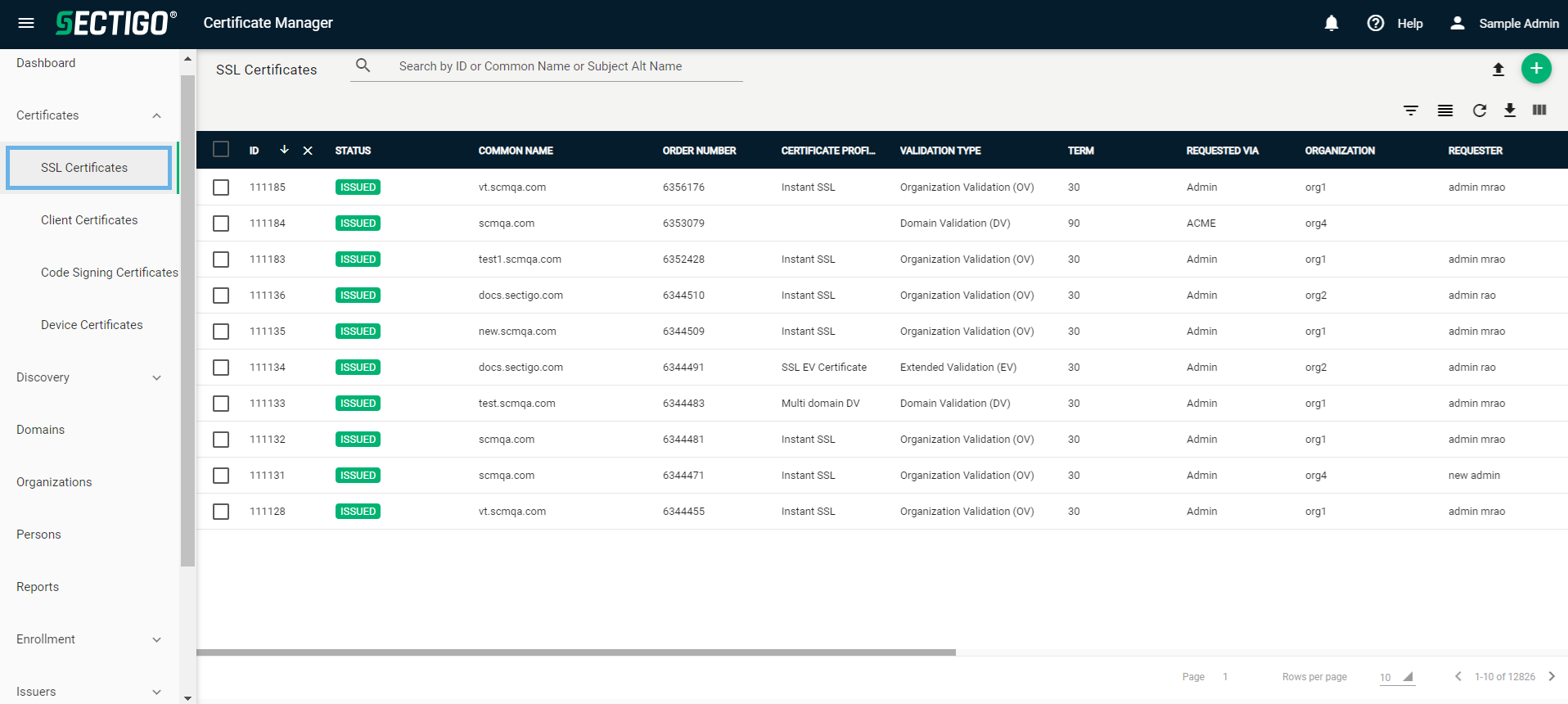
The following table describes the details and controls of the SSL Certificates page.
| Column | Description |
|---|---|
ID |
The unique numeric identifier of the certificate. |
Status |
The status of the certificate. The possible values are:
|
Common name |
The domain name used during the SSL certificate request. This refers to the common name in the certificate itself. |
Order number |
The unique identifier created by the issuing CA to represent the certificate request. |
Certificate profile |
The certificate profile used for the certificate request. |
Validation type |
The level of validation performed by the CA when issuing the certificate. The possible values are:
|
Term |
The validity period of the certificate. |
Requested via |
The method used to request the certificate or to bring it into SCM. The possible values are:
|
Organization |
The organization that requested or has been issued the certificate. |
Department |
The department, if any, that requested or has been issued the certificate. |
Requester |
The email address of the end-user, or the name of the administrator who requested the certificate. |
Approver |
The name of the administrator who approved the certificate request. |
Subject |
The entity (such as a domain, organization, individual, or device) identified by the certificate, containing unique attributes that distinguish it from others. |
City |
The city where the associated organization or department is located. |
State |
The state or province where the associated organization or department is located. |
Country |
The country where the associated organization or department is located. |
Subject alt name |
Additional names or attributes that identify the entity associated with the certificate. Subject Alternative Names (SANs) can include alternative domain names, email addresses, IP addresses, or other identifiers relevant to SSL certificates. |
SAN Count |
The number of SANs included in the certificate. |
Licensed SAN |
The number of licensed SANs for the certificate. |
Issuer |
The name of the certificate and the issuing CA. |
Expires |
The date that the certificate expires. |
Serial number |
A unique serial number assigned to the certificate. |
Key usage |
The cryptographic operations that the certificate is valid for. |
Extended key usage |
Additional cryptographic operations that the certificate is valid for. |
Key algorithm |
The algorithm used to generate the key pair. |
Key size / curve |
The size of the key pair or the curve used to generate the key pair. |
Signature algorithm |
The algorithm used to sign the certificate. |
MD5 hash |
The MD5 hash (thumbprint/fingerprint) of the certificate. |
SHA1 hash |
The SHA1 hash (thumbprint/fingerprint) of the certificate. |
Comments |
Comments or notes about the certificate. |
Requested |
The date that the certificate was requested. |
Approved |
The date that the certificate was approved. |
Declined |
The date that the certificate request was declined. |
Issued |
The date that the certificate was issued. |
Downloaded |
The date that the certificate was downloaded. |
Discovered |
The date that the certificate was discovered. |
Revoked |
The date that the certificate was revoked. |
Replaced |
The date that the certificate was replaced. |
External requester |
The email address of any external requester(s). This is either manually entered by an administrator requesting the certificate on behalf of an external user, or populated with email address(es) found in the Subject DN (Email field) and/or Subject Alternative Name (SAN) extension during certificate discovery. |
Private key |
Indicates whether the private key is stored in a private key store (PKS). The possible values are:
|
Install state |
Indicates the current state of scheduled certificate auto-installation. The possible values are:
|
Renewal state |
Indicates the current state of scheduled certificate auto-renewal. The possible values are:
|
Renewed |
The date that the certificate was renewed. |
Custom fields |
Depending on your configuration, various custom field columns may be available containing additional information about the certificate. |
Table controls |
|
Quick Search |
Enables you to quickly search the results by ID, Common Name, or Subject Alternative Name. |
Filter |
Enables you to sort the table information using custom filters. |
Group |
Enables you to sort the table information using predefined groups. |
Refresh |
Refreshes the information presented in the table. |
Download CSV |
Downloads the table information as a |
Manage Columns |
Enables you to select which table columns to display. |
Admin controls |
|
Add |
Opens the Request SSL Certificate dialog where you can request a new certificate. |
Import |
Opens the Import SSL Certificate dialog where you can manually import a certificate to SCM. |
Delete |
Opens the Delete Certificate dialog where you can delete the certificate entry from SCM. |
Edit |
Opens the Edit SSL Certificate dialog where you can edit the details of the certificate request. |
View |
Opens the SSL Certificate page where you can view certificate details and perform various administrative tasks (such as, resending collection emails or downloading the certificate). |
Approve |
Opens the Approve Message dialog where you can approve the certificate request. |
Decline |
Opens the Decline Message dialog where you can decline the certificate request. |
Install |
Opens the Certificate auto-installation dialog where you can initiate certificate auto-installation. |
Revoke |
Opens the Revocation Reason dialog where you can revoke the certificate. |
Renew |
Opens the Renew Certificate dialog where you can renew the certificate. |
Mark Renewed |
Opens the Mark Certificate as Renewed dialog where you can manually mark the certificate as renewed. |
Replace |
Opens the Replace Certificate dialog where you can replace the existing certificate. |
View Audit |
Opens the Certificate Audit page where you can view or download audit logs. |
Enrollment methods
SCM supports the enrollment of SSL certificates using the following methods:
-
Enrollment Wizard — Enroll SSL certificates through the SCM enrollment wizard. For more information, see Enroll an SSL certificate in SCM.
-
Bulk Enrollment — Enroll multiple SSL certificates at once, using a bulk enrollment form. For more information, see Understanding bulk SSL enrollment.
-
Self-Enrollment — Manually enroll SSL certificates using a self-enrollment form outside of SCM. For more information, see Understanding enrollment forms.
-
MS agent — Enroll SSL certificates through Microsoft Active Directory Certificate Services (AD CS) using a configured SCM MS agent. For more information, see Understanding MS agents.
-
EST — Enroll SSL certificates through the Enrollment over Secure Transport (EST) protocol using a configured SCM EST endpoint. For more information, see Understanding EST endpoints.
-
REST API — Enroll SSL certificates through the SCM REST API using a configured SCM REST API endpoint. For more information, see Understanding REST endpoints.
-
Admin API — Enroll SSL certificates through the SCM Admin API using a configured SCM API Admin. For more information, see Understanding administrators.
-
CA connector — Enroll SSL certificates through a third-party CA using a configured SCM CA connector. For more information, see Understanding CA connectors.
-
ACME — Enroll SSL certificates through the Automated Certificate Management Environment (ACME) protocol using a configured SCM ACME endpoint. For more information, see Understanding ACME endpoints.