Database Settings
Use the Database Settings page to configure both SMART Database Scan and Database Backup options for your website.
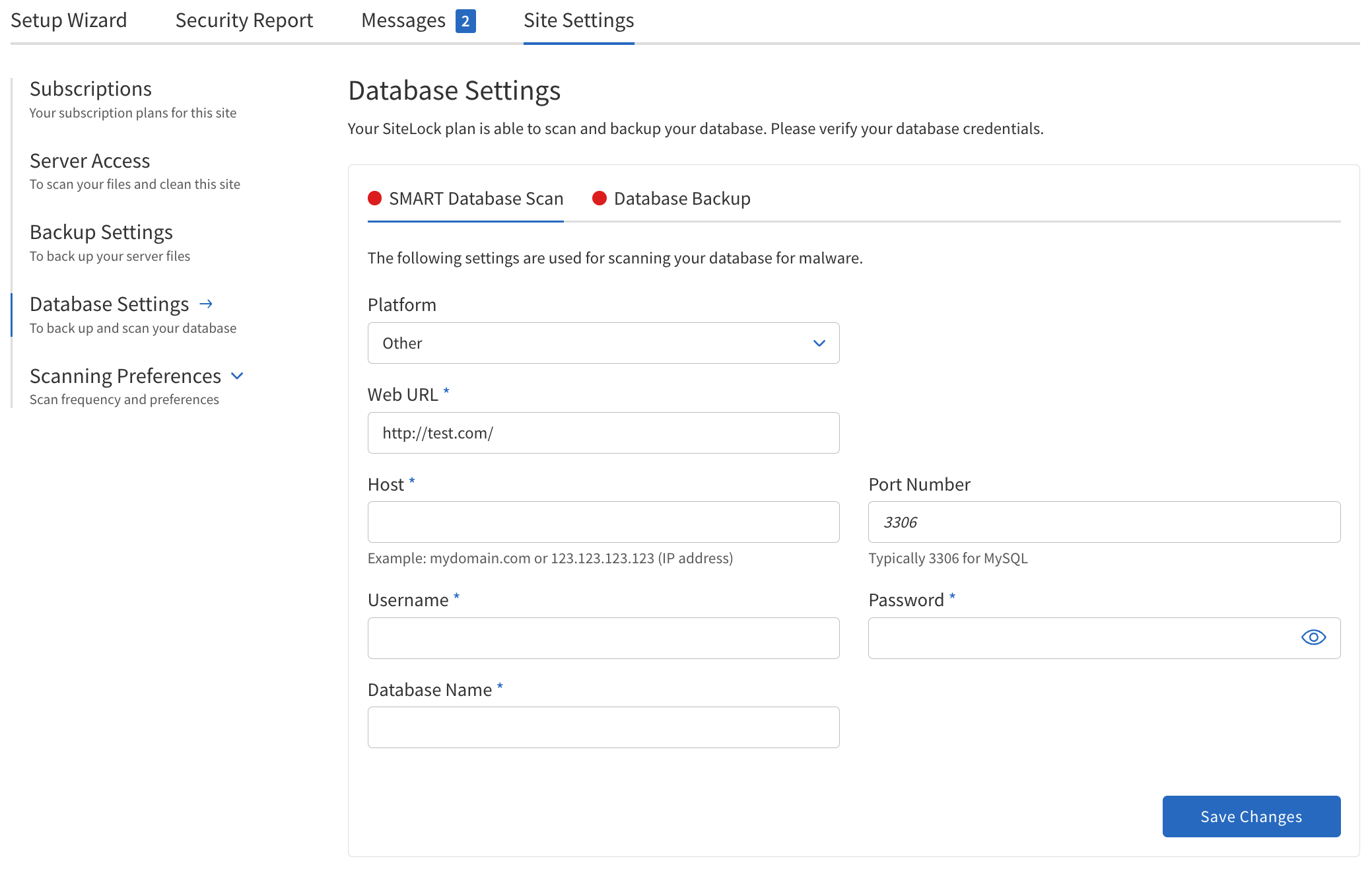
SMART Database Scan
The SMART Database Scan feature allows you to scan your website’s database for malware, vulnerabilities, and suspicious content.
The following table describes the details of the SMART Database Scan section:
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
Platform |
Select the platform the website is using.
|
Web URL |
The URL of the website. Example: |
Host |
The IP address or hostname of the server. Example: |
Port Number |
The port used to connect to the database. This is the port number of the MySQL server. Typically, |
Username |
The name of the database user. |
Password |
The password required for database access. |
Database Name |
The name of the database to be scanned. |
Status indicators |
Colors indicate status of each tab.
|
Configuring SMART Database Scan
To configure a scan:
-
Navigate to .
-
Select your website platform from the list. If your site uses WordPress or Joomla, database credentials are detected automatically. For other platforms, enter the credentials manually.
-
Enter the full web URL of your site.
-
Provide the database host (server address or IP).
-
Specify the port number used by your database server (default is
3306for MySQL). -
Enter the database username and password.
-
Specify the name of the database you want to scan.
-
Review the status indicators to ensure all required fields are configured (green means configured, red means attention needed).
-
Click Save Changes to apply your settings.
These settings enable the system to connect securely to your database and perform regular scans for threats.
Database Backup
Database backup can also be configured in Server Access.
The following table describes details of the Database Backup section.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
Database Backup Frequency |
Select how often to back up the database.
|
Web URL |
The URL of the website. Example: |
Host |
The server address where the MySQL server operates. Example: Typically, localhost. |
Port Number: |
The port used to connect to the database. Typically, |
Username |
The FTP username |
Password |
The password required for database access. |
Database Name |
The name of the database to be backed up. |
Functionality |
Status indicators.
|
Configuring Database Backups
To configure database backups:
-
In the Database Backup section, choose how often you want backups to occur from the Database Backup Frequency list.
-
Enter the full web URL of your site.
-
Provide the database host (server address or IP).
-
Specify the port number used by your database server (default is
3306for MySQL). -
Enter the FTP username and password for backup storage access.
-
Specify the name of the database you want to back up.
-
Review the status indicators to ensure all required fields are configured (green means configured, red means attention needed).
-
Click Save Changes to apply your backup settings.
These settings ensure your database is regularly backed up according to your selected schedule. Backups are stored securely and can be restored if needed.