Using the connector
You can enroll and install a certificate on the Nginx web server. The Lego client automatically modifies your web server’s configuration to install a certificate and enable SSL.
Enroll a certificate
Execute the lego command from the /etc/lego directory to enroll a certificate.
lego --server https://acme-qa.secure.trust-provider.com/v2/DV --email [email protected] --accept-tos --domains example.com --eab --kid JfGQUcPqpUE_eIzROsiNEg --hmac YLVw7sj5cj5EurPd_DgoqkKOrjJJWUu7b9Xp6i_jKlTyc-PSpRn0woCVra-LrRUfiEAoV3rKFS4wZfqXh5nbaA --key-type rsa2048 --http runlego --server https://acme-qa.secure.trust-provider.com/v2/DV --email --email [email protected] --accept-tos --domains example.com --domains www.example.com --domains blog.example.com --eab --kid JfGQUcPqpUE_eIzROsiNEg --hmac YLVw7sj5cj5EurPd_DgoqkKOrjJJWUu7b9Xp6i_jKlTyc-PSpRn0woCVra-LrRUfiEAoV3rKFS4wZfqXh5nbaA --key-type rsa2048 --http run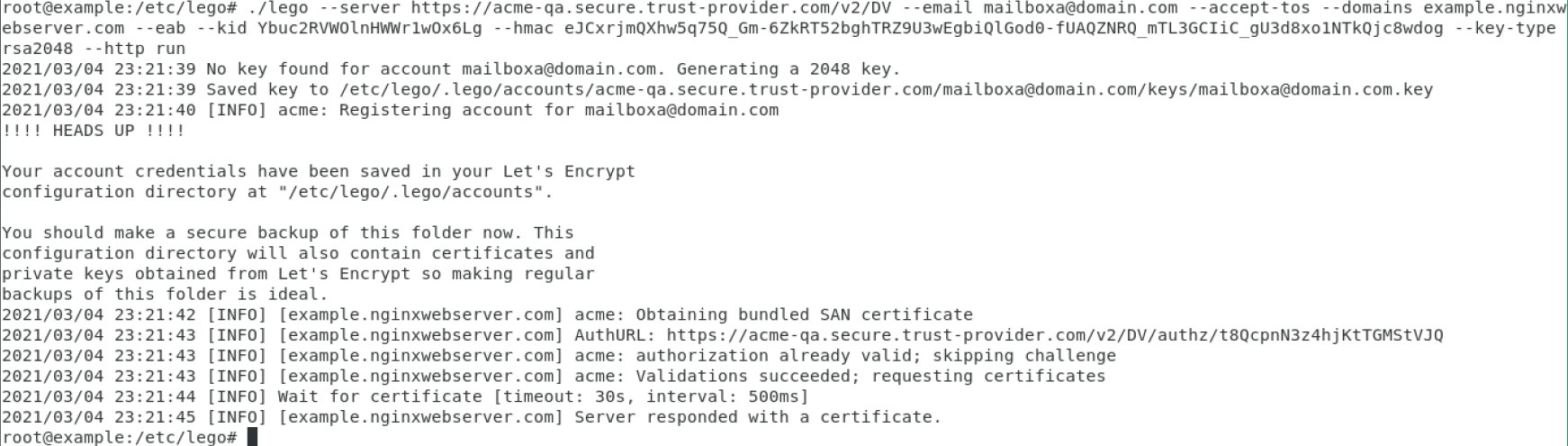
The enrolled certificates in PEM format are placed in the etc/lego/.lego/certificates directory.
The following files are created as part of the certificate issuance:
-
example.example.com.crt: The full certificate chain
-
example.example.com.com.issuer.crt: The CA certificate(s)
-
example.example.com.com.key: The private key
|
You can use the |
The following table describes the basic command-line options for the client. A complete list of Lego options can be found in the documentation.
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
|
The ACME server URL for DV/EV/OV SSL certificates |
|
Indicates that you agree to the Sectigo ACME terms of service |
|
The email address for registration and recovery contact |
|
Uses External Account Binding for account registration |
|
The key ID for external account binding |
|
The HMAC key for external account binding |
|
Use the HTTP-01 challenge |
|
Registers an account, then creates and installs a certificate |
|
Renews a certificate |
Enable auto-renewal
You can create a cronjob that will invoke the script on a schedule (see crontab for cron schedule expressions) to check whether the certificate is eligible for renewal:
-
Run
crontab -eon the terminal. -
Add a cronjob that will trigger the script.
The following example will trigger the client every week.
0 0 * * 7 cd /etc/lego && lego --server https://acme-qa.secure.trust-provider.com/v2/DV --email [email protected] --domains example.com --http renew --key-type rsa2048
Enable SSL on Nginx
-
Open the
/etc/nginx/sites-available/defaultfile in your preferred editor. -
Add the numbered lines.
nano/etc/nginx/sites-available/default server { listen 80 default_server; listen [::]:80 default server; listen 443 ssl default_server; (1) listen [::]:443 ssl default_server; (2) ssl_certificate /etc/lego/.lego/certificates/example.com.crt; (3) ssl_certificate_key /etc/lego/.lego/certificates/example.com.key; (4) root /var/www/html; index index.html index.htm index.ngin-debian.html; server_name _; access log /var/log/nginx/nginx.vhost.access.log; error_log /var/log/nginx/nginx.vhost.error.log; location / { try files $uri/ =404; } }1 Enables SSL on port 443 2 Enables 443 on all IP addresses associated with the web server 3 Associates the server certificate to the web server 4 Associates the server private key to the web server -
Save and close the file.
-
Restart the Nginx service.
systemctl restart nginx
| To verify the installation, open a browser and visit your website using the HTTPS protocol—the domain should be enabled with a locked padlock which means the website is SSL enabled. |